Objectives
- Set-up a cylindrical projection over the United States.
- Apply land-shading on the coastlines.
- Load a grib file containing Mean-Sea level Presssure and visualise it using black isolines.
- Load a grib file containing Precipitation and visualise it using shading technique.
- Add a legend.
- Add a text.
- Draw the position of New-York City
- Draw a line to materialise the Xsection we are going to visualise in a next tutorial
You will need to download
|
|
|
Setting of the geographical area
The Geographical area we want to work with today is defined by its lower-left corner [20oN, 110oE] and its upper-right corner [70oN, 30oE].
Have a look at the subpage documentation to learn how to setup a projection .
subpage_lower_left_longitude | | subpage_lower_left_latitude | | subpage_upper_right_longitude | | subpage_upper_right_latitude |
|
from Magics.macro import *
#setting the output
output = output(
output_formats = ['png'],
output_name = "map_step1",
output_name_first_page_number = "off"
)
#settings of the geographical area
area = mmap(subpage_map_projection="cylindrical",
subpage_lower_left_longitude=-110.,
subpage_lower_left_latitude=20.,
subpage_upper_right_longitude=-30.,
subpage_upper_right_latitude=70.,
)
#Using a default coastlines to see the result
plot(output, area, mcoast()) |
|
|
Setting the coastlines
Until now you have used the mcoast to add coastlines to your plot. The mcoast object comes with a lot of parameters to allow you to style your coastlines layer.
The full list of parameters can be found in the Coastlines documentation.
In this first exercise, we will like to see:
- The land coloured in cream.
- The coastlines in grey.
- The grid as a grey dash line.
map_coastline_land_shade | | map_coastline_land_shade_colour | | map_coastline_colour | | map_grid_colour | | map_grid_line_style |
|
from Magics.macro import *
#setting the output
output = output(
output_formats = ['png'],
output_name = "map_step2",
output_name_first_page_number = "off"
)
#settings of the geographical area
area = mmap(subpage_map_projection="cylindrical",
subpage_lower_left_longitude=-110.,
subpage_lower_left_latitude=20.,
subpage_upper_right_longitude=-30.,
subpage_upper_right_latitude=70.,
)
#settings of the caostlines
coast = mcoast(map_coastline_land_shade = "on",
map_coastline_land_shade_colour = "cream",
map_grid_line_style = "dash",
map_grid_colour = "grey",
map_label = "on",
map_coastline_colour = "grey")
plot(output, area, coast) |
|
|
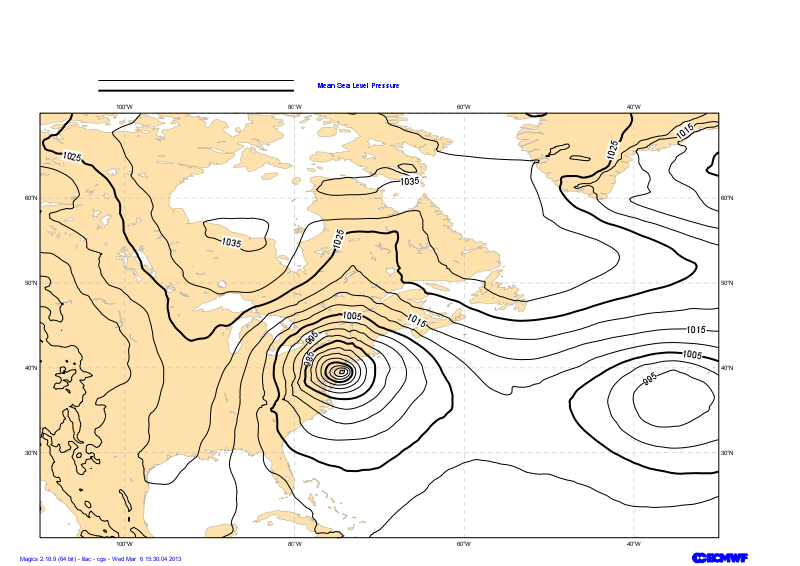
Visualising the Mean Sea Level Pressure field
The visualisation of any data in Magics is done by combining 2 kind of objects. One, the Data Action, is used to define the data and explain to Magics how to interpret it, the other one is called Visual Action and will define the type of visualisation and its attributes.
In this example our data are in a grib file msl.grib. The Data Action to be used is mgrib in is documented in Grib Input Documentation.
The Visualisation we want to apply is a basic contouring, using black for the lines and an interval of 5 hPa, between isolines. We also want to add a automatic legend, with our own text "Mean Sea Level Pressure". Follow the link to access the Contouring Documentation.
mgrib action to load the data |
|---|
| grib_input_file_name |
| mcont action to define a contouring |
|---|
| contour_line_colour | | contour_line_thickness | | contour_highlight_colour | | contour_highlight_thickness | | contour_hilo | | contour_level_selection_type | | contour_interval | | legend | | contour_legend_text |
|
from Magics.macro import *
#setting the output
output = output(
output_formats = ['png'],
output_name = "map_step3",
output_name_first_page_number = "off"
)
#settings of the geographical area
area = mmap(subpage_map_projection="cylindrical",
subpage_lower_left_longitude=-110.,
subpage_lower_left_latitude=20.,
subpage_upper_right_longitude=-30.,
subpage_upper_right_latitude=70.,
)
#settings of the caostlines
coast = mcoast(map_coastline_land_shade = "on",
map_coastline_land_shade_colour = "cream",
map_grid_line_style = "dash",
map_grid_colour = "grey",
map_label = "on",
map_coastline_colour = "grey")
#Loading the msl Grib data
msl = mgrib(grib_input_file_name="msl.grib")
#Defining the controur
contour = mcont(contour_highlight_colour= "black",
contour_highlight_thickness= 4,
contour_hilo= "off",
contour_interval= 5.,
contour_label= "on",
contour_label_frequency= 2,
contour_label_height= 0.4,
contour_level_selection_type= "interval",
contour_line_colour= "black",
contour_line_thickness= 2,
legend='on',
contour_legend_text= "Mean Sea Level Pressure",
)
plot(output, area, coast) |
|
 |
|
Adding a text
Magics allows the user to add of or several lines of text. The position of the text is by default above the plot, but some parameters aloow it to be moved around.
A basic html formatting can be used for colour, style, and font size.
The mtext object has to be inserted in the plot command to see the text on the result.
from Magics.macro import *
#settings of the png output
output = output(
output_formats = ['png'],
output_name = "coast",
output_name_first_page_number = "off"
)
##settings of the coastlines attributes
coast = mcoast(
map_coastline_land_shade = "on",
map_coastline_land_shade_colour = "cream",
map_grid_line_style = "dash",
map_grid_colour = "brown",
map_label_colour = "brown",
map_coastline_colour = "brown"
)
##settings of the text (notice the Html formatting)
title = mtext(
text_lines = ["Hello World!", " <b>This is my first plot</b> !"],
text_font_size = "0.7",
text_colour = "charcoal"
)
#The plot command will now use the coast and title objects
plot(output, coast, title) |
|