| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
| Column |
|---|
| | Panel |
|---|
Objectives
- Set-up a cylindrical projection over the United States.
- Apply land-shading on the coastlines.
- Load a grib GRIB file containing Mean-Sea level Presssure and visualise it using black isolines.
- Load a grib GRIB file containing Precipitation and visualise it using shading technique.
- Add a legend.Add a text.
- Draw the position of New-York City
- Draw a line to materialise the Xsection we are going to visualise in a next tutorial
- Add a text.
You will need to download
|
|
|
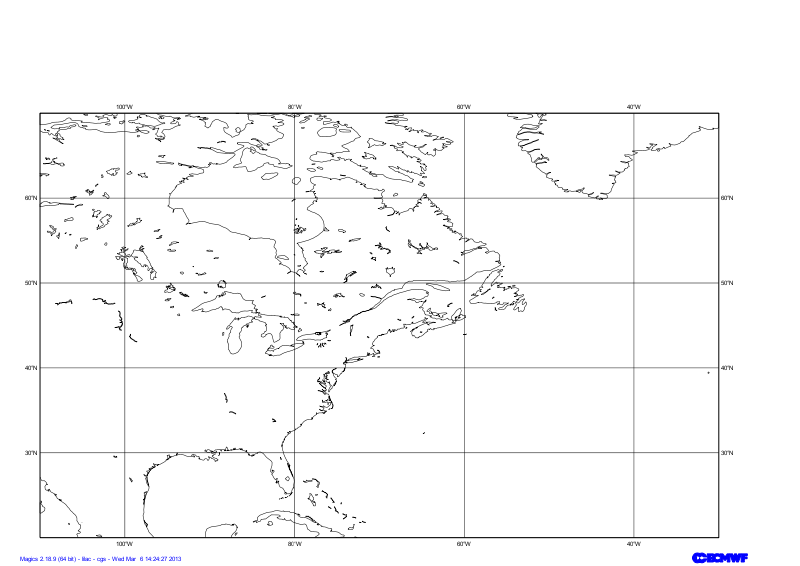
Setting of the geographical area
The Geographical geographical area we want to work with today is defined by its lower-left corner [20oN, 110oEW] and its upper-right corner [70oN, 30oEW].
Have a look at the subpage documentation to learn how to setup a projection .
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| | Info |
|---|
|
| Useful subpage parameters |
|---|
subpage_lower_left_longitude | | subpage_lower_left_latitude | | subpage_upper_right_longitude | | subpage_upper_right_latitude |
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| theme | Confluence |
|---|
| language | python |
|---|
| title | Python - Setting a projection |
|---|
| collapse | true |
|---|
| from Magics.macro import *
#setting the output
output = output(
output_formats = ['png'],
output_name = "map_step1",
output_name_first_page_number = "off"
)
#settings of the geographical area
area = mmap(subpage_map_projection="cylindrical",
subpage_lower_left_longitude=-110.,
subpage_lower_left_latitude=20.,
subpage_upper_right_longitude=-30.,
subpage_upper_right_latitude=70.,
)
#Using a default coastlines to see the result
plot(output, area, mcoast()) |
|
| Column |
|---|
| 
|
|
...
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| | Info |
|---|
|
| Useful Coastlines parameters |
|---|
map_coastline_land_shade | | map_coastline_land_shade_colour | | map_coastline_colour | | map_grid_colour | | map_grid_line_style |
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| theme | Confluence |
|---|
| language | python |
|---|
| title | Python - Coastlines |
|---|
| collapse | true |
|---|
| from Magics.macro import *
#setting the output
output = output(
output_formats = ['png'],
output_name = "map_step2",
output_name_first_page_number = "off"
)
#settings of the geographical area
area = mmap(subpage_map_projection="cylindrical",
subpage_lower_left_longitude=-110.,
subpage_lower_left_latitude=20.,
subpage_upper_right_longitude=-30.,
subpage_upper_right_latitude=70.,
)
#settings of the caostlines
coast = mcoast(map_coastline_land_shade = "on",
map_coastline_land_shade_colour = "cream",
map_grid_line_style = "dash",
map_grid_colour = "grey",
map_label = "on",
map_coastline_colour = "grey")
plot(output, area, coast) |
|
| Column |
|---|
|  |
|
...
The visualisation of any data in Magics is done by combining 2 kind of objects. One, the Data Action, is used to define the data and explain to Magics how to interpret it, the other one is called Visual Action and will define the type of visualisation and its attributes.
In this example our data are in a grib GRIB file msl.grib. The Data Action to be used is mgrib in is documented in Grib Input Documentation.
The Visualisation visualisation we want to apply is a basic contouring mcont, using black for the lines and . We want an interval of 5 hPa , between isolines. We also want to add a an automatic legend, with our own text "Mean Sea Level Pressure". Follow the link to access the Contouring Documentation.
...
The goal of this exercise is to discover a bit more the diverse styles of visualisation offered by the mcont object.
We are pre-processed grib a GRIB field containing the precipitation accumulated in the last 6 hours of the valid time. We want to disable the automatic scaling appled by Magics and use our own scaling factor, in this case 1000.
...
The position of New York is [7441oEN, 4174oNW], we can give this position to Magics using the minput object, documented in Input Data Page.
...
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| | Info |
|---|
|
| Useful input parameters |
|---|
input_x_values | | input_y_values |
| Useful Symbol parameters |
|---|
| symbol_colour | | symbol_marker_index | | symbol_height | symbol_type | | symbol_text_list | | symbol_text_font_size | | symbol_text_font_colour | | symbol_text_font_style | | symbol_text_position |
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| theme | Confluence |
|---|
| language | python |
|---|
| title | Python - Adding New- Overlay York City |
|---|
| collapse | true |
|---|
| from Magics.macro import *
#setting the output
output = output(
output_formats = ['png'],
output_name = "map_step6",
output_name_first_page_number = "off"
)
#---------------------------------------
# definition of the previsous layers
# ...
# ...
#---------------------------------------
#definition of New-York city
new_york = minput(
input_x_values = [-74.],
input_y_values = [41.]
)
#definition of the symbol
point = msymb(
symbol_type = "both",
symbol_text_list = ["NYC"],
symbol_marker_index = 28,
symbol_colour = "red",
symbol_height = 0.5,
symbol_text_font_size = 0.40,
symbol_text_font_colour = "black",
symbol_text_position = "top",
symbol_text_font_style = "bold ",
)
plot(output, area, coast, precip, shading, msl, contour, new_york, point, legend) |
|
| Column |
|---|
|  |
|
...
Adding a line to show our next Cross-section
In the next exercise, we will display a Cross-section of the Vorticity across the Storm.
We want to show this line of our plot as a black thick line.
The stating point is [50oN, 90oW], the end point is [30oN, 60oW] : it can be passed to Magics using the minput object, documented in Input Data Page.
To draw the line we will use the mgraph object. All the parameters are available in the Graph Plotting Documentation.
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| | Info |
|---|
|
| Useful input parameters |
|---|
input_x_values | | input_y_values |
| Useful Graph parameters |
|---|
| graph_line | | graph_line_colour |
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| theme | Confluence |
|---|
| language | python |
|---|
| title | Python - Adding a line |
|---|
| collapse | true |
|---|
| from Magics.macro import *
#setting the output
output = output(
output_formats = ['png'],
output_name = "map_step7",
output_name_first_page_number = "off"
)
#---------------------------------------
# definition of the previous layers
# ...
# ...
#---------------------------------------
#definition of the Xsection Line
xsection = minput(
input_x_values = [-90., -60.],
input_y_values = [50., 30.]
)
#definition of the graph
line = mgraph(
graph_line_colour = "black",
graph_line_thickness = 4
)
plot(output, area, coast, precip, shading, msl, contour, new_york, point, xsection, line, legend) |
|
| Column |
|---|
|  Image Added Image Added |
|
Adding a title
We have now a very nice plot... let's add a title at the top.
Text box can be embedded everywhere on a plot, but the default position will be a title at the top of the plot, above an potential legend.
The text facility is documented in the Text Plotting Page.
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
| | Info |
|---|
|
| Useful Text parameters |
|---|
text_lines | | text_font_size | | text_colour | | text_font_style |
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| theme | Confluence |
|---|
| language | python |
|---|
| title | Python - Adding a text |
|---|
| collapse | true |
|---|
| from Magics.macro import *
#setting the output
output = output(
output_formats = ['png'],
output_name = "map_step8",
output_name_first_page_number = "off"
)
#---------------------------------------
# definition of the previous layers
# ...
# ...
#---------------------------------------
#definition of the text
title = mtext(text_lines=['Sandy', '30th of October 2012'],
text_font_size = 0.8,
text_colour= "charcoal",
text_font_style='bold',
)
plot(output, area, coast, precip, shading, msl, contour, new_york, point, xsection, line, legend, title) |
|
| Column |
|---|
|  Image Added Image Added |
|
Go to the next step...
Go back to the main page ...





