| Section | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Setting of the geographical area
The Geographical area we want to work with today is defined by its lower-left corner [20oN, 110oE] and its upper-right corner [70oN, 30oE].
Have a look at the subpage documentation to learn how to setup a projection .
Profile: create the Cartesian Projection
For our vertical profile, we will need :
- a horizontal regular axis for a temperature range going from -60oC to 20oC.
- a vertical logarithmic axis going from 1020 hPa to 10 hPa
Have a look at the Subpage Documentation and at the Axis Plotting Documentation, and try to get the 0oC grid line highlighted.
| Section | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
Setting the coastlines
Until now you have used the mcoast to add coastlines to your plot. The mcoast object comes with a lot of parameters to allow you to style your coastlines layer.
The full list of parameters can be found in the Coastlines documentation.
In this first exercise, we will like to see:
The land coloured in cream.
The coastlines in grey.
The grid as a grey dash line.
Useful Coastlines parameters
map_coastline_land_shade
map_coastline_land_shade_colour
map_coastline_colour
map_grid_colour
map_grid_line_style
from Magics.macro import * #setting the output output = output( output_formats = ['png'], output_name = "map_step2", output_name_first_page_number = "off" ) #settings of the geographical area area = mmap(subpage_map_projection="cylindrical", subpage_lower_left_longitude=-110., subpage_lower_left_latitude=20., subpage_upper_right_longitude=-30., subpage_upper_right_latitude=70., ) #settings of the caostlines coast = mcoast(map_coastline_land_shade = "on", map_coastline_land_shade_colour = "cream", map_grid_line_style = "dash", map_grid_colour = "grey", map_label = "on", map_coastline_colour = "grey") plot(output, area, coast)
Visualising the Mean Sea Level Pressure field
The visualisation of any data in Magics is done by combining 2 kind of objects. One, the Data Action, is used to define the data and explain to Magics how to interpret it, the other one is called Visual Action and will define the type of visualisation and its attributes.
In this example our data are in a grib file msl.grib. The Data Action to be used is mgrib in is documented in Grib Input Documentation.
The Visualisation we want to apply is a basic contouring, using black for the lines and an interval of 5 hPa, between isolines. We also want to add a automatic legend, with our own text "Mean Sea Level Pressure". Follow the link to access the Contouring Documentation.
mgrib action to load the data
grib_input_file_name
mcont action to define a contouring
contour_line_colour
contour_line_thickness
contour_highlight_colour
contour_highlight_thickness
contour_hilo
contour_level_selection_type
contour_interval
legend
contour_legend_text
from Magics.macro import * #setting the output output = output( output_formats = ['png'], output_name = "map_step3", output_name_first_page_number = "off" ) #settings of the geographical area area = mmap(subpage_map_projection="cylindrical", subpage_lower_left_longitude=-110., subpage_lower_left_latitude=20., subpage_upper_right_longitude=-30., subpage_upper_right_latitude=70., ) #settings of the caostlines coast = mcoast(map_coastline_land_shade = "on", map_coastline_land_shade_colour = "cream", map_grid_line_style = "dash", map_grid_colour = "grey", map_label = "on", map_coastline_colour = "grey") #Loading the msl Grib data msl = mgrib(grib_input_file_name="msl.grib") #Defining the controur contour = mcont(contour_highlight_colour= "black", contour_highlight_thickness= 4, contour_hilo= "off", contour_interval= 5., contour_label= "on", contour_label_frequency= 2, contour_label_height= 0.4, contour_level_selection_type= "interval", contour_line_colour= "black", contour_line_thickness= 2, legend='on', contour_legend_text= "Mean Sea Level Pressure", ) plot(output, area, coast, msl, contour)
Visualising the precipitation field
The goal of this exercise is to discover a bit more the diverse styles of visualisation offered by the mcont object.
We are pre-processed grib field containing the precipitation accumulated in the last 6 hours of the valid time. We want to disable the automatic scaling appled by Magics and use our own scaling factor, in this case 1000.
Here we will work with shading, and we will use a different technique to setup the levels we want to contour.
We want to use the following list of levels for contouring [0.5, 2., 4., 10., 25., 50., 100., 250.]
and the following list of colours ["cyan", "greenish_blue", "blue", "bluish_purple", "magenta", "orange", "red", "charcoal"]
mgrib action to load the data
grib_input_file_name
grib_automatic_scaling
grib_scaling_factor
mcont action to define a contouring
contour_level_selection_type
contour_level_list
contour_shade
contour_shade_method
contour_shade_colour_method
contour_level_selection_type
contour_shade_colour_list
legend
#setting the output output = output( output_formats = ['png'], output_name = "map_step4", output_name_first_page_number = "off" ) #settings of the geographical area area = mmap(subpage_map_projection="cylindrical", subpage_lower_left_longitude=-110., subpage_lower_left_latitude=20., subpage_upper_right_longitude=-30., subpage_upper_right_latitude=70., ) #settings of the caostlines coast = mcoast(map_coastline_land_shade = "on", map_coastline_land_shade_colour = "cream", map_grid_line_style = "dash", map_grid_colour = "grey", map_label = "on", map_coastline_colour = "grey") #definition of the input data precip = mgrib(grib_input_file_name="precip.grib", grib_automatic_scaling='off', grib_scaling_factor=1000.) shading = mcont( contour_highlight= "off", contour_hilo= "off", contour_label="off", contour_level_list=[0.5, 2., 4., 10., 25., 50., 100., 250.], contour_level_selection_type= "level_list", contour_shade= "on", contour_shade_method= "area_fill", contour_shade_colour_method= "list", contour_shade_colour_list= ["cyan", "greenish_blue", "blue", "bluish_purple", "magenta", "orange", "red", "charcoal"], legend="on") plot(output, area, coast, precip, shading)
Overlaying the 2 layers and playing with legend
Here, we want to demonstrate the plot command.
The actions added to the plot command will be executed sequentially, and their result will be displayed from the background to the foreground .
Then, try to put the shaded layer (precipitation) behind the contoured layer (msl)
and try to improve the legend to make it look continuous, by checking the Legend Documentation.
Useful legend parameters
legend
legend_display_type
legend_text_colour
legend_text_font_size
from Magics.macro import * #setting the output output = output( output_formats = ['png'], output_name = "map_step5", output_name_first_page_number = "off" ) #settings of the geographical area area = mmap(subpage_map_projection="cylindrical", subpage_lower_left_longitude=-110., subpage_lower_left_latitude=20., subpage_upper_right_longitude=-30., subpage_upper_right_latitude=70., ) #settings of the caostlines coast = mcoast(map_coastline_land_shade = "on", map_coastline_land_shade_colour = "cream", map_grid_line_style = "dash", map_grid_colour = "grey", map_label = "on", map_coastline_colour = "grey") #definition of the input data precip = mgrib(grib_input_file_name="precip.grib", grib_automatic_scaling='off', grib_scaling_factor=1000.) #definition of shading shading = mcont( contour_highlight= "off", contour_hilo= "off", contour_label="off", contour_level_list=[0.5, 2., 4., 10., 25., 50., 100., 250.], contour_level_selection_type= "level_list", contour_shade= "on", contour_shade_method= "area_fill", contour_shade_colour_method= "list", contour_shade_colour_list= ["cyan", "greenish_blue", "blue", "bluish_purple", "magenta", "orange", "red", "charcoal"], legend="on") #definition of msl msl = mgrib(grib_input_file_name="msl.grib") #Definition of the black contouring contour = mcont( contour_highlight_colour= "black", contour_highlight_thickness= 4, contour_hilo= "off", contour_interval= 5., contour_label= "on", contour_label_frequency= 2, contour_label_height= 0.4, contour_legend_text= "Mean Sea Level Pressure", contour_level_selection_type= "interval", contour_line_colour= "black", contour_line_thickness= 2, legend='on' ) #Definition of the legend legend = mlegend(legend='on', legend_display_type='continuous', legend_text_colour='charcoal', legend_text_font_size=0.4, ) plot(output, area, coast, precip, shading, msl, contour, legend)
Adding the position of New York City
To demonstrate the use of symbols plotting, we are going to add a big red dot where New York City is.We will the add the text NYC in black on top of the dot.
The position of New York is [41oN, 74oE], we can give this position to Magics using the minput object, documented in Input Data Page.
The symbol is performed using the msymb object. You can find the full options in the Symbol Documentation.
Useful input parameters
input_x_values
input_y_values
Useful Symbol parameters
symbol_colour
symbol_marker_index
symbol_height
symbol_type
symbol_text_list
symbol_text_font_size
symbol_text_font_colour
symbol_text_font_style
symbol_text_position
from Magics.macro import * #setting the output output = output( output_formats = ['png'], output_name = "map_step6", output_name_first_page_number = "off" ) #--------------------------------------- # definition of the previsous layers # ... # ... #--------------------------------------- #definition of New-York city new_york = minput( input_x_values = [-74.], input_y_values = [41.] ) #definition of the symbol point = msymb( symbol_type = "both", symbol_text_list = ["NYC"], symbol_marker_index = 28, symbol_colour = "red", symbol_height = 0.5, symbol_text_font_size = 0.40, symbol_text_font_colour = "black", symbol_text_position = "top", symbol_text_font_style = "bold ", ) plot(output, area, coast, precip, shading, msl, contour, new_york, point, legend)
Adding a line to show our next Cross-section
In the next exercise, we will display a Cross-section of the Vorticity across the Storm.
We want to show this line of our plot as a black thick line.
The stating point is [50oN, 90oE], the end point is [30oN, 60oE] : it can be passed to Magics using the minput object, documented in Input Data Page.
To draw the line we will use the mgraph object. All the parameters are available in the Graph Plotting Documentation.
Useful input parameters
input_x_values
input_y_values
Useful Graph parameters
graph_line
graph_line_colour
from Magics.macro import * #setting the output output = output( output_formats = ['png'], output_name = "map_step7", output_name_first_page_number = "off" ) #--------------------------------------- # definition of the previous layers # ... # ... #--------------------------------------- #definition of the Xsection Line xsection = minput( input_x_values = [-74.], input_y_values = [41.] ) #definition of the graph line = mgraph( graph_line_colour = "black", graph_line_thickness = 4 ) plot(output, area, coast, precip, shading, msl, contour, new_york, point, xsection, line, legend)
Adding a title
We have now a very nice plot... let's add a title at the top.
Text box can be embedded everywhere on a plot, but the default position will be a title at the top of the plot, above an potential legend.
The text facility is documented in the Text Plotting Page.
Useful Text parameters
text_lines
text_font_size
text_colour
text_font_style
from Magics.macro import * #setting the output output = output( output_formats = ['png'], output_name = "map_step8", output_name_first_page_number = "off" ) #--------------------------------------- # definition of the previous layers # ... # ... #--------------------------------------- #definition of the text title = mtext(text_lines=['Sandy', '30th of October 2012'], text_font_size = 0.8, text_colour= "charcoal", text_font_style='bold', ) plot(output, area, coast, precip, shading, msl, contour, new_york, point, xsection, line, legend, title)
|
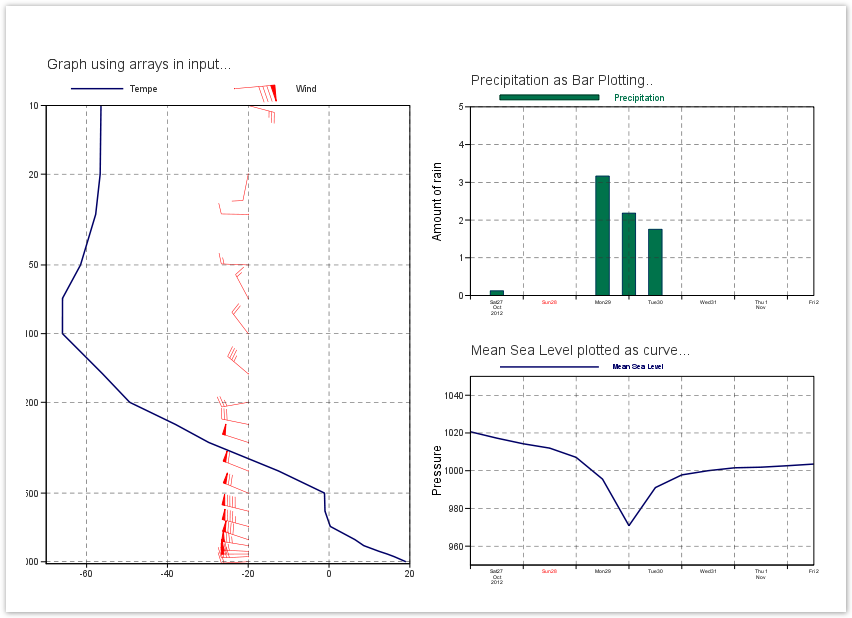
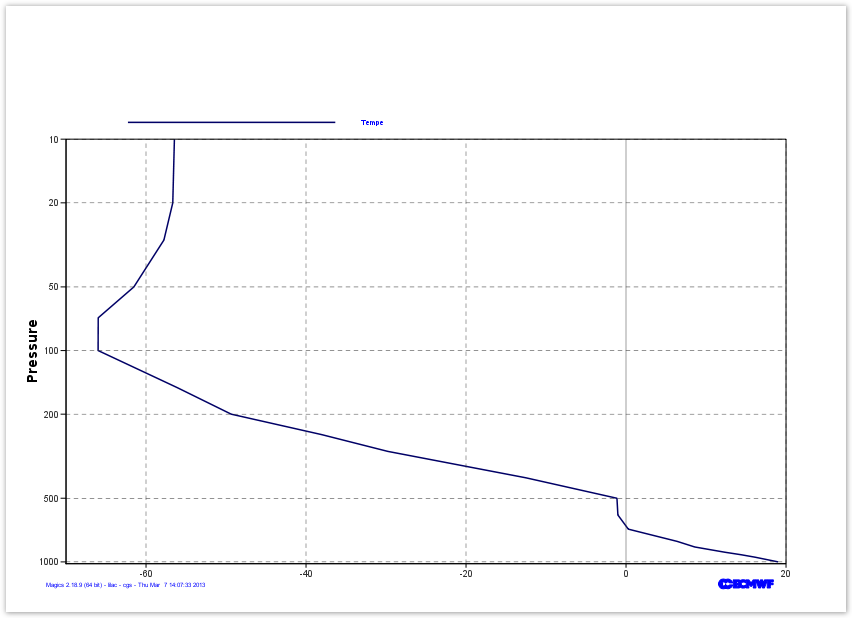
Profile: Using Arrays as Input of a Graph
Here is the list of levels, and the list of Temperature in Kelvin at each levels.
levels = [1.,2.,3,5,7,10,20,30,50,70,100,150,200,250,300,400,500,600,700,800,850,900,925,950,1000]kelvin = ([263.118652344,254.822738647,242.517868042,223.301025391,219.254943848,216.710174561,216.507095337, 215.398986816,211.643295288,207.18812561,207.172134399,217.097396851,223.809326172,235.13168335,243.377059937,260.635147095,272.02935791,272.145584106,273.448501587,279.562927246,281.745040894,285.503082275,287.543685913,289.284072876,292.170974731]We can pass these arrays to Magics using the minput object . Check the Input Data Documentation for more information about the parameters. Note that we want to use Celsius in our graph...
The mgraph object can then be used to preform the visualisation. All the parameters can be found in the Graph Plotting Page.
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
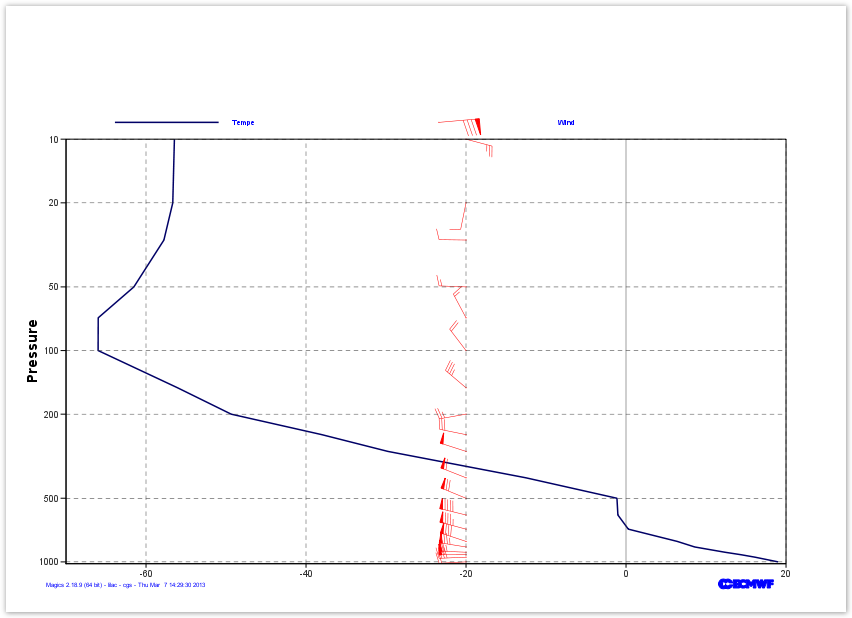
Profile: Using Arrays as Input for wind Plotting
Here is the list of pressure levels, and the list of u and v components for each pressure level.
levels = [1.,2.,3,5,7,10,20,30,50,70,100,150,200,250,300,400,500,600,700,800,850,900,925,950,1000]u_component = [77.815612793,63.232711792,44.9090881348,28.2789916992,17.401763916, 11.8307037354,-0.725036621094,-4.75889587402,-7.83796691895,-3.76489257812, -6.18388366699,-13.1139526367,-13.05027771,-15.1851959229,-23.5844726562, -27.866394043,-33.0458984375,-45.8946380615,-41.540222168,-39.6210327148, -37.6231689453,-32.947265625,-29.4743499756,-22.0828552246,-10.0008392334]v_component = [7.38911437988,5.23355102539,0.636322021484,-3.75567626953, 0.167388916016,-3.12893676758,-3.60003662109,0.0688171386719, 0.305236816406,7.06889343262,8.10516357422,11.1141815186, -2.29931640625,3.08065795898,7.5965423584,11.0112915039, 13.6437530518,11.2753143311,11.1552124023,13.1494903564, 6.01538085938,1.37588500977,-0.0724334716797,-0.953598022461,-0.508377075195]We can pass these arrays to Magics using the minput object . Check the Input Data Documentation for more information about the parameters.
We want to plot these winds as red flags on the vertical of -20.
The mgraph object can then be used to preform the visualisation. All the parameters can be found in the Graph Plotting Page.
Do not forget to add a legend with some meaningful text!
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Time Series: Setting the Cartesian Projection for the Mean Sea Level Pressure time series
In this exercise, we will learn how to setup a date Coordinate, and browse the parameters available to style the style a date axis.
We want
- a horizontal date axis going from the 2012-10-27at 00:00:00 to 2012-11-02 12:00:00
- a vertical regular axis going from 950 hPa to 1050 hPa
Have a look at the Subpage Documentation and at the Axis Plotting Documentation,
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
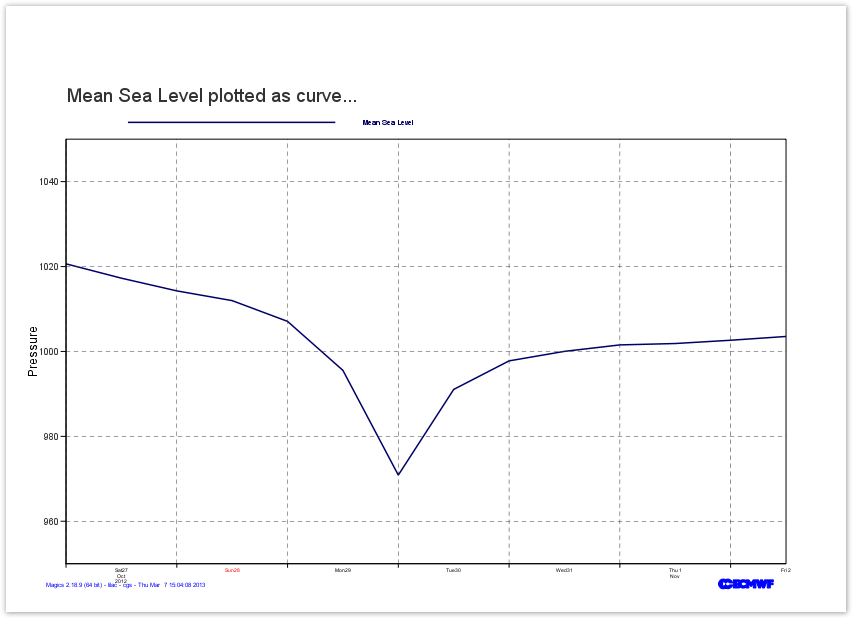
Time Series: Using a CSV file as input of a curve
The values for our time series are in CSV (Comma-Separeted-Value) ascii file called msl.csv.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
1,2012-10-27 00:00:00,1020.64125,0
2,2012-10-27 12:00:00,1017.261875,0.1220703125
3,2012-10-28 00:00:00,1014.27125,-9.58071727163e-21
4,2012-10-28 12:00:00,1011.97375,-2.80979885101e-20 |
The valid date is defined in the second column, the value of msl in the third.
This information need to be given to Magics . This can be done with the mtable data action,. See the full documentation.
The mgraph action will then be used to define the curve attributes. All the parameters can be found in the Graph Plotting Page.
You can always add a title using the mtext object.
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
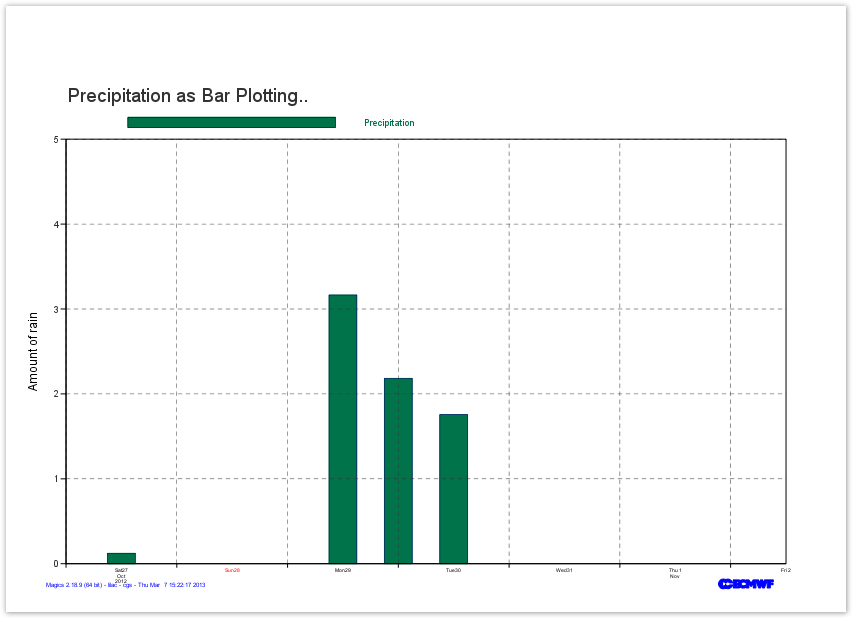
Time Series : Using Automatic Axis and bar plotting
Magics can automatically set-up the coordinates system according to the plotted data.
In this exercise, we will use this functionality to draw the time series of the precipitation.
- The horizontal date coordinate system is set automatically.
- The vertical coordinate system is regular going from 0 to 5
The data will be pass to Magics using arrays:
dates = ["2012-10-27 00:00:00","2012-10-27 12:00:00","2012-10-28 00:00:00", "2012-10-28 12:00:00","2012-10-29 00:00:00","2012-10-29 12:00:00", "2012-10-30 00:00:00","2012-10-30 12:00:00", "2012-10-31 00:00:00","2012-10-31 12:00:00", "2012-11-01 00:00:00","2012-11-01 12:00:00", "2012-11-02 00:00:00","2012-11-02 12:00:00"]precip = [0.,0.1220703125,0.,0., 0., 3.16429138184, 2.18200683594,1.75476074219,0,0,0,0,0,0.]We want to display the information using bar plotting.
We will perhaps need to check quickly
- The Subpage Documentation
- The Axis Documentation
- The Input Data Documentation
- The Graph Plotting Documentation
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Finally, A bit of layout ...
On our image, we want to create 3 pages.. We will use the pseudo action page to do that..
| Gliffy Diagram | ||
|---|---|---|
|
The position of the page is set with the 4 following parameters
- page_x_position / page_y_position : to position in cm the bottom left corner of the page in its parent
- page_x_length / page_y_length : the dimension in cm.
The drawing area ( where the plotting is rendered) is called subpage and can position into the page using the 4 following parameters
- subpage_x_position / subpage_y_position : to position in cm the bottom left corner of the drawing area (subpage) in its parent page.
- subpage_x_length / subpage_y_length : the dimension in cm.
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Go to to the Main Magics Tutorial